Sandalwood oil has captivated hearts and souls across centuries, serving not only as a fragrant delight but also as a vital component in various cultural and medicinal practices. Its enchanting aroma has made it a key player in rituals, skincare, and aromatherapy, each use steeped in rich tradition and history.
The story of sandalwood oil begins with its origins in ancient civilizations, where it was revered for its calming properties and unique scent. As we delve deeper into this remarkable oil, we’ll uncover the methods of its extraction, its therapeutic benefits, and its ecological impacts, revealing why it remains a beloved staple in many cultures today.
The origins and historical significance of sandalwood oil are essential to understand its value.
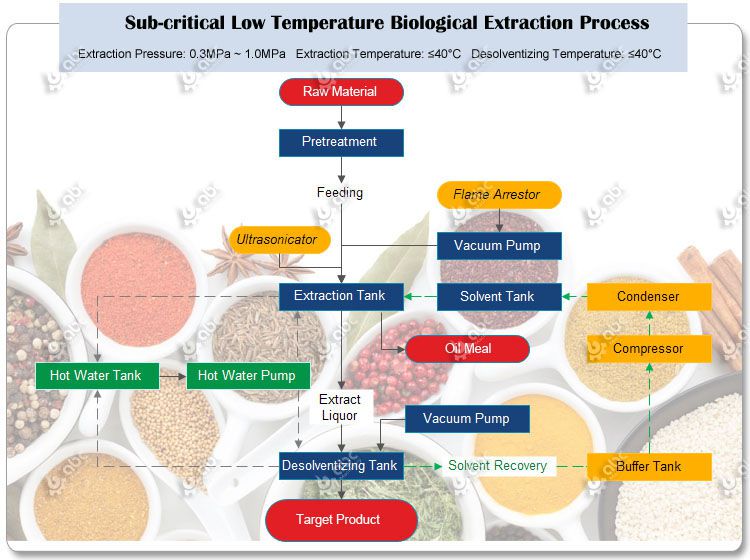
Sandalwood oil, derived from the heartwood of the sandalwood tree, has been revered for centuries across various cultures due to its unique fragrance and therapeutic properties. Its origins trace back to ancient civilizations, where it was not only a prized commodity but also held spiritual significance. Understanding the historical context of sandalwood oil offers valuable insight into its contemporary relevance and enduring allure.
The historical uses of sandalwood oil are diverse, reflecting its importance in rituals, medicine, and daily life in various cultures. In ancient India, sandalwood was integral to religious and spiritual practices. It was commonly used in Hindu rituals, where it symbolized purity and was believed to promote a connection between the earthly and divine. Additionally, the oil was incorporated in Ayurveda, the traditional Indian system of medicine, for its calming properties and to treat various ailments.
Historical uses of sandalwood oil in ancient civilizations
The utilization of sandalwood oil transcends geographical boundaries, with many cultures incorporating it into their practices. The following points highlight its historical significance:
- In ancient Egyptian culture, sandalwood was used in embalming practices, believed to aid in the afterlife and provide a fragrant scent to the deceased.
- In Chinese traditional medicine, sandalwood oil was valued for its ability to alleviate mental disorders and was often applied in treatments for anxiety and depression.
- The ancient Greeks used sandalwood oil in perfumes and cosmetics, recognizing its alluring scent and skin-soothing properties.
- In Indigenous cultures of Australia, various parts of the sandalwood tree, including the oil, have been used for medicinal purposes and in ceremonial practices, emphasizing its role in cultural heritage.
The perception and utilization of sandalwood oil have varied significantly among different cultures. For instance, in many Southeast Asian countries, it was often associated with luxury and was traded along ancient trade routes, making it a symbol of wealth. In contrast, indigenous practices often revolve around its spiritual significance, where the oil is used in rituals to promote harmony and well-being.
“Sandalwood oil has been referred to as the ‘soul of the sandalwood tree,’ representing a bridge between the physical and spiritual realms.”
Traditional practices involving sandalwood oil include its use in religious ceremonies and therapeutic applications. In Buddhist traditions, the scent of sandalwood is believed to enhance meditation, fostering tranquility and focus. Furthermore, in Ayurvedic medicine, it serves as a natural remedy for skin conditions and is used in formulations aimed at promoting emotional balance and relaxation.
Overall, the historical significance of sandalwood oil is deeply embedded in the cultural practices of various societies, underscoring its enduring value across generations. Its multifaceted use—ranging from spiritual to medicinal—demonstrates a rich tapestry of beliefs and traditions that continue to influence its application in modern times.
The extraction methods of sandalwood oil play a crucial role in determining its quality.
The extraction of sandalwood oil is a vital process influencing its aroma, therapeutic properties, and overall quality. Various methods are employed to derive this precious oil from the heartwood of the sandalwood tree, each method having its unique characteristics, advantages, and drawbacks. Understanding these methods is essential for anyone interested in the intricacies of sandalwood oil production and its applications in perfumery, aromatherapy, and traditional medicine.
Sandalwood oil can be extracted using several methods, primarily steam distillation and solvent extraction. Each technique carries its own set of benefits and limitations, which ultimately affect the quality and aromatic properties of the oil produced.
Steam Distillation
Steam distillation is the most common method used for extracting sandalwood oil. This technique involves passing steam through the wood, which vaporizes the volatile compounds. The vapor is then condensed back into liquid form, allowing the oil to be collected.
- Advantages:
- Produces high-quality oil with a complex aromatic profile.
- Preserves the natural constituents of sandalwood, enhancing its therapeutic properties.
- Environmentally friendly, as it does not require the use of harmful solvents.
- Disadvantages:
- Requires significant amounts of raw material, leading to potential sustainability issues.
- Can be expensive due to the energy required for the distillation process.
- Time-consuming, as the process can take several hours to complete.
The aromatic properties of sandalwood oil obtained through steam distillation are rich and well-rounded, making it highly sought after in perfumery and aromatherapy. The method retains the delicate balance of the wood’s scent profile, characterized by its warm, creamy, and slightly sweet aroma.
Solvent Extraction
Solvent extraction is another prevalent method for extracting sandalwood oil, especially when high yields are needed. In this process, organic solvents are used to dissolve the oil from the wood, after which the solvent is evaporated to leave behind the concentrated oil.
- Advantages:
- Higher yield compared to steam distillation, allowing for more oil extraction from the same amount of wood.
- Can extract a wider range of aromatic compounds, capturing nuances that steam distillation might miss.
- Faster than steam distillation, reducing the overall production time.
- Disadvantages:
- May alter the natural aroma and therapeutic properties of the oil due to the use of solvents.
- Potential health risks associated with residual solvent in the final product, which may raise safety concerns.
- Environmental impacts due to the use of chemicals that require careful disposal.
Sandalwood oil extracted via solvent methods may exhibit a different aromatic profile, often described as more intense and less nuanced than that produced by steam distillation. This can sometimes result in a less desirable oil for high-end perfumery applications, where subtlety is important.
Ultimately, the choice of extraction method significantly influences the quality, aroma, and applications of sandalwood oil. Each method has its place in the market, catering to different needs and preferences, ensuring that both therapeutic and aromatic qualities can be appreciated in this sought-after essential oil.
The therapeutic properties of sandalwood oil contribute to its popularity in aromatherapy.
Sandalwood oil has long been revered for its calming and grounding effects, making it a staple in the world of aromatherapy. This essential oil, derived from the heartwood of sandalwood trees, boasts a rich history of use in various cultures for its therapeutic properties. Its warm, woody aroma not only enhances the ambiance of spaces but also promotes emotional and physical well-being, which explains its enduring popularity among aromatherapy enthusiasts.
The main therapeutic benefits of sandalwood oil include its ability to reduce anxiety, improve sleep quality, and enhance mood. Its calming effects make it particularly beneficial for individuals dealing with everyday stressors. Research indicates that sandalwood oil can help lower cortisol levels, the hormone associated with stress, leading to a more relaxed state of mind. Additionally, the oil’s anti-inflammatory and antiseptic properties position it as a natural choice for skincare and overall wellness practices.
Applications of sandalwood oil in aromatherapy
Sandalwood oil is widely utilized in various aromatherapy practices due to its versatile nature and therapeutic advantages. Here are some common applications that highlight its significance:
- Diffusion: Sandalwood oil can be added to essential oil diffusers, filling the environment with its soothing aroma. This practice is known to enhance relaxation during meditation or yoga sessions, creating a peaceful atmosphere.
- Massage: When mixed with a carrier oil, sandalwood oil can be used for therapeutic massages. The calming scent and skin-nourishing properties help relieve tension and promote a sense of well-being.
- Baths: Adding a few drops of sandalwood oil to bathwater transforms a regular bath into a calming retreat, aiding in relaxation and stress relief after a long day.
Scientific studies have provided substantial evidence supporting the therapeutic claims of sandalwood oil. For instance, a study published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology highlighted the anxiolytic (anxiety-reducing) effects of sandalwood oil, demonstrating its capability to promote relaxation through aroma inhalation. Another research piece in the Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine suggested that inhalation of sandalwood oil can improve mood and decrease feelings of tension during stressful situations.
“The aroma of sandalwood oil has been reported to have significant effects on mood enhancement and anxiety reduction, making it a valuable tool in holistic health practices.”
Overall, the extensive therapeutic properties of sandalwood oil contribute to its esteemed status in the realm of aromatherapy, attracting those seeking natural solutions for mental and emotional challenges.
The applications of sandalwood oil in skincare products highlight its versatility.
Sandalwood oil is renowned for its aromatic properties and therapeutic benefits, making it a popular ingredient in various skincare formulations. Its versatility stems from its ability to cater to diverse skin concerns, ranging from hydration to soothing irritation. Incorporating sandalwood oil into skincare can enhance product efficacy and user experience, establishing it as a staple in many beauty regimens.
Sandalwood oil is commonly found in numerous skincare formulations, each designed to target specific skin issues. Some of these formulations include moisturizers, serums, facial oils, and masks. Its incorporation is not only due to its pleasant scent but also because of its beneficial properties for the skin. Below are some common formulations that prominently feature sandalwood oil:
- Moisturizers – Providing hydration while imparting a calming effect on the skin.
- Serums – Targeting specific concerns like uneven skin tone and blemishes.
- Facial Oils – Offering nourishment and promoting a radiant complexion.
- Face Masks – Delivering intensive treatment for soothing and revitalizing the skin.
Benefits of sandalwood oil for different skin types
Sandalwood oil is particularly beneficial for various skin types due to its unique properties. Its moisturizing and anti-inflammatory characteristics make it suitable for dry, oily, and sensitive skin alike. The following Artikels how sandalwood oil can cater to distinct skin types:
- Dry Skin: Sandalwood oil helps in deeply hydrating and nourishing the skin, preventing flakiness and dryness.
- Oily Skin: Its astringent properties assist in regulating sebum production, helping to reduce excess oiliness while maintaining moisture balance.
- Sensitive Skin: Sandalwood oil’s soothing properties make it excellent for calming irritated or inflamed skin, alleviating redness and discomfort.
- Combination Skin: It strikes a balance by hydrating dry patches while controlling oiliness in certain areas.
Interactions with other ingredients in skincare products
Sandalwood oil’s versatility extends to its compatibility with a variety of other skincare ingredients. When formulated with other components, it can enhance their effectiveness and bolster the overall skin benefits. Here are some key interactions observed in skincare products:
- Vitamin E: When combined with vitamin E, sandalwood oil provides enhanced antioxidant protection, promoting healthier skin.
- Aloe Vera: This pairing is excellent for hydration; aloe vera’s soothing properties complement sandalwood oil’s calming effects.
- Tea Tree Oil: Together, they form a powerful blend for acne treatment, combining sandalwood’s anti-inflammatory properties with tea tree oil’s antibacterial action.
- Hyaluronic Acid: Their combination results in deep moisture retention, enhancing the skin’s plumpness and elasticity.
“Sandalwood oil not only enhances the fragrance of skincare formulations but also contributes to their therapeutic properties, making it a versatile ingredient across various products.”
The ecological impact of sandalwood oil production raises important sustainability concerns.
The production of sandalwood oil is not only notable for its aromatic properties but also for the environmental challenges it poses. Sandalwood trees, primarily Santalum album, are slow-growing and faced with the threat of over-exploitation due to their high demand. This extraction process raises significant sustainability and ecological concerns that must be addressed to ensure the long-term viability of sandalwood resources and the surrounding ecosystems.
The cultivation and harvesting of sandalwood trees lead to various environmental challenges, largely due to unsustainable practices. Deforestation, habitat destruction, and soil degradation are common outcomes when sandalwood is harvested without considering ecological balance. The tree’s reliance on host plants for water and nutrients means that poor management can disrupt entire ecosystems. Furthermore, illegal logging practices exacerbate these issues, contributing to biodiversity loss in regions where sandalwood is indigenous. The economic pressures on local communities can often lead to a disregard for sustainable practices, which ultimately puts the sandalwood species at risk.
Implementation of sustainable practices in sandalwood oil production
Adopting sustainable practices in sandalwood oil production is crucial for mitigating the ecological impact of harvesting. Various practices can be put into place to ensure that sandalwood cultivation does not harm the environment. These include:
- Plantation management: Establishing controlled plantations that responsibly manage the growth of sandalwood trees, ensuring that they are harvested at the right time and not over-extracted.
- Agroforestry systems: Integrating sandalwood cultivation with other crops can enhance biodiversity and soil health, providing a sustainable habitat for various species while ensuring economic returns.
- Community involvement: Engaging local communities in sustainable harvesting practices can empower them economically and raise awareness of the importance of conservation efforts.
- Certification programs: Encouraging certifications such as Fair Trade or Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) can help ensure that sandalwood products are sourced sustainably and ethically.
The ecological footprints of sandalwood oil compared to synthetic alternatives reveal significant differences in environmental impact. While sandalwood oil production can lead to deforestation and habitat loss, synthetic alternatives often rely on petroleum-based chemicals, which contribute to pollution and greenhouse gas emissions during their production.
Natural sandalwood oil, when sustainably sourced, often has a lower carbon footprint than its synthetic counterparts, which require significant energy inputs and can emit harmful pollutants.
Real-life examples highlight this contrast. For instance, some brands have successfully transitioned to sustainable sandalwood sourcing, resulting in a smaller ecological footprint compared to synthetic fragrance manufacturers. In places like India and Australia, organizations are working to revitalize sandalwood populations through sustainable practices, showcasing the potential for harmony between economic development and ecological preservation.
The global market for sandalwood oil is influenced by various economic factors.
Sandalwood oil, prized for its aromatic and therapeutic properties, has seen a dynamic evolution in its global market. The demand for this essential oil is shaped by a blend of cultural practices, industrial applications, and economic trends. As consumer preferences shift towards natural and sustainable products, sandalwood oil’s appeal continues to grow, influencing its market trajectory significantly.
Current consumption trends in sandalwood oil reflect a burgeoning interest in aromatherapy, personal care, and wellness industries. This oil has carved a niche in various regions, driven by both traditional uses and modern applications. The rise in health consciousness and preference for natural ingredients in cosmetics and fragrances has led to an increase in demand. Notably, Asia-Pacific remains a significant market due to its cultural heritage tied to sandalwood, while the North American and European markets are witnessing a steady increase in consumption fueled by wellness trends.
Pricing dynamics of sandalwood oil
The pricing of sandalwood oil is complex and influenced by multiple economic factors, including supply constraints, production costs, and market demand. Sandalwood oil is one of the most expensive essential oils, primarily due to its slow growth cycle and the limited availability of mature sandalwood trees. The price per liter can vary drastically based on the quality of the oil and its geographical origin.
Several factors affect the market value of sandalwood oil:
- Supply and Demand: The scarcity of sandalwood trees, particularly those sourced from Santalum album, has led to higher prices. Demand from emerging markets also contributes to price inflation.
- Production Costs: Factors such as labor costs, land use, and cultivation practices impact the overall cost of sandalwood oil production. Sustainable harvesting practices can also require investments that influence pricing.
- Quality Variations: The oil’s aroma and therapeutic properties vary by region and quality, leading to different pricing tiers within the market.
The price per liter of high-quality sandalwood oil can reach as high as $200 to $300 or more.
Major producers and consumers of sandalwood oil
The sandalwood oil market is characterized by significant geographical disparities in production and consumption. Key producing countries include India, Australia, and Indonesia, each contributing to the global supply through unique cultivation practices and species.
In terms of major consumers, the following insights highlight the landscape:
- India: As the largest producer and consumer, India has a long tradition of using sandalwood oil in religious rituals, cosmetics, and perfumes.
- Australia: Gaining recognition for producing high-quality sandalwood oil, particularly from the Santalum spicatum species, Australia is becoming a significant player in the global market.
- United States: The U.S. market is increasingly consuming sandalwood oil, driven by the demand for natural products in personal care and aromatherapy.
- China: As a growing market, China’s interest in sandalwood oil is largely influenced by traditional medicine and wellness practices.
Understanding the dynamics of the sandalwood oil market is critical for stakeholders navigating this evolving landscape, as economic factors continually shape the industry’s future.
The role of sandalwood oil in cultural and spiritual practices is profound and noteworthy.
Sandalwood oil has held a significant place in various cultures and spiritual traditions around the world. Its deep, woody aroma and rich history make it an essential component in many religious ceremonies and spiritual practices. From ancient rituals to modern mindfulness techniques, sandalwood oil continues to symbolize purity, offering a connection to the divine and enhancing meditative states.
Sandalwood oil is revered for its calming properties, making it a popular choice in religious and spiritual practices across different cultures. It is often used in ceremonies to purify spaces, invoke spirituality, and enhance the atmosphere of devotion. The oil is extracted from the heartwood of sandalwood trees, which are primarily found in India, Australia, and Indonesia, adding to its sacred appeal.
Significance of Sandalwood Oil in Religious Ceremonies
Sandalwood oil is integral to various cultural rituals, with its significance varying across different religious practices. It is commonly used in Hinduism, Buddhism, and certain Indigenous traditions, reflecting its cross-cultural importance.
– Hindu Ceremonies: In Hindu rituals, sandalwood oil is applied to deities and used in offerings, symbolizing purity and devotion. It is believed to attract positive energy and divine blessings.
– Buddhist Practices: Buddhists utilize sandalwood oil in meditation and prayer, as its fragrance is thought to aid concentration and mindfulness. It is often burned as incense during meditation sessions to create a tranquil environment.
– Indigenous Spirituality: Many Indigenous cultures incorporate sandalwood oil in their sacred rituals, utilizing it for its spiritual cleansing properties. It is often used in smudging ceremonies to purify and bless spaces.
The use of sandalwood oil in these religious ceremonies emphasizes its role in enhancing spiritual experiences and fostering a deeper connection to the sacred.
Utilization in Meditation and Mindfulness Practices
The calming aroma of sandalwood oil plays a crucial role in meditation and mindfulness practices, contributing to a serene and focused environment. The oil is used in various ways to enhance spiritual practices and promote relaxation.
– Aromatherapy: Sandalwood oil is a popular choice in aromatherapy. Its soothing scent helps reduce anxiety and stress, making it easier for individuals to enter a meditative state.
– Meditation Tools: Many practitioners incorporate sandalwood oil into their meditation routines by applying it to pulse points or using it in diffuser blends to create a calming atmosphere.
– Mindfulness Rituals: Incorporating sandalwood oil into daily mindfulness rituals can enhance the experience. Its calming properties help individuals center their thoughts and promote a sense of overall well-being.
Through these practices, sandalwood oil becomes more than just an aromatic substance; it becomes a tool for spiritual growth and emotional balance.
Cultural Rituals Featuring Sandalwood Oil
Sandalwood oil is embedded in numerous cultural rituals, reflecting its significance across various societies. These rituals highlight the oil’s role in enhancing spiritual connection and fostering community bonds.
– Chandan Yatra: In Hinduism, the Chandan Yatra is a ritual where sandalwood paste is applied to deities, celebrating its cooling properties and symbolizing purity and devotion.
– Buddhist Sandalwood Offerings: During worship, Buddhists offer sandalwood flowers and incense to the Buddha, illustrating respect and devotion. The scent is believed to purify the surroundings and elevate the spiritual ambiance.
– Ceremonial Smudging: Many Indigenous cultures utilize sandalwood oil in smudging ceremonies, where the smoke is believed to carry prayers to the spirit world, purifying and blessing the participants and space.
These cultural rituals demonstrate how sandalwood oil transcends its physical properties, acting as a bridge between the material and spiritual worlds.
Closure

As we’ve explored, sandalwood oil is not just an aromatic treat; it’s a blend of culture, history, and modern application. From its sacred uses in spiritual practices to its role in skincare and wellness, sandalwood oil continues to hold a significant place in our lives, urging us to consider sustainability in its production and consumption for generations to come.
FAQ Resource
What are the most common uses of sandalwood oil?
Sandalwood oil is commonly used in aromatherapy, skincare products, and religious rituals, appreciated for its calming and soothing properties.
Is sandalwood oil safe for all skin types?
Generally, sandalwood oil is safe for most skin types, but it’s advisable to conduct a patch test before widespread use, particularly for sensitive skin.
Can sandalwood oil help with anxiety?
Yes, many users report that sandalwood oil helps reduce anxiety and promotes relaxation, making it a popular choice in aromatherapy.
How does sandalwood oil compare to synthetic fragrances?
Sandalwood oil is more natural and typically has a richer, more complex scent profile compared to synthetic fragrances, which can be harsh and less nuanced.
Where is sandalwood oil predominantly sourced from?
Australia, India, and Hawaii are some of the major regions known for producing high-quality sandalwood oil.
